Choosing a tech career can feel overwhelming. The two trending career paths in coding are Full Stack Development and Web Development.
Both are rewarding, but they focus on different skills and responsibilities.
Having a clear understanding of Full Stack vs Web Development is the first step towards picking the correct career path.
What is Full Stack Development?
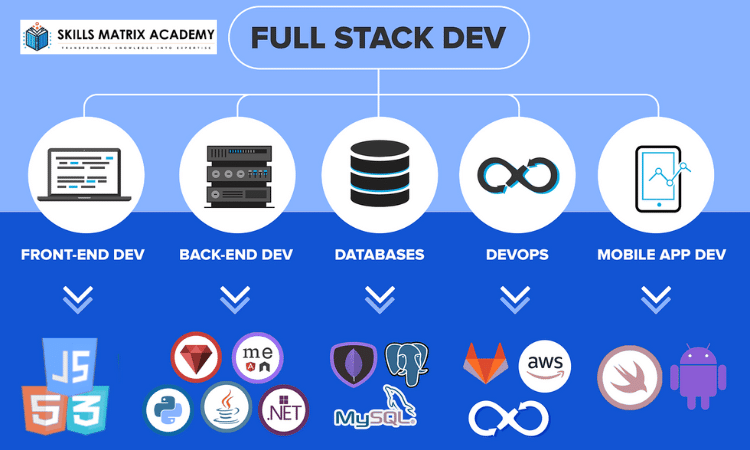
Full Stack Development handles both the front end (what users see) and the back end (server operations) of applications.
Full-stack developers don’t just build websites. They handle:
- Entire web applications
- Databases
- Server-side technologies like the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache Web Server, MySQL, PHP)
This makes them versatile in software development. They are comfortable with:
- Server operating systems
- Web server administration
- Building secure, reliable applications
Who Are Full Stack Developers?
Full-stack developers are multi-skilled professionals who work on both frontend and backend development to build functional, user-friendly systems.
What makes them stand out is their ability to use multiple programming languages such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, C++, and Python. They also understand frameworks, platforms, and databases, which allows them to handle projects from start to finish.
From brainstorming ideas to final deployment, full-stack developers play an active role in production planning. They can also troubleshoot and solve technical issues at any stage of development.
Beyond coding, full-stack developers collaborate with design teams to transform prototypes into working products. They stay updated with industry trends and new technologies,
ensuring the applications they build remain secure and high-performing. Regular maintenance, upgrades, and skill improvement are also part of their role, helping them stay ahead in a fast-changing tech world.
Technologies in Full Stack Development
1. Frontend Technologies in Full Stack Development
The front end handles everything users view and engage with. It’s about creating smooth user experiences and polished website designs.
Frontend developers focus on: Website structure, Website functionality, and User interaction.
This side uses essential programming languages and tools. Let’s break them down.
- HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language): HTML is the foundation of all websites, structuring their content and layout.It structures each page and links it with others. Without HTML, there’s no web design or development.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets):CSS makes websites visually appealing. It controls colors, fonts, and layouts. By decoupling design and content, CSS enhances functionality and facilitates user-friendly interfaces.
- JavaScript (JS): JavaScript brings websites to life. It powers dynamic pages, interactive features, and even web-based apps or games. JS ensures smooth interaction and modern, engaging interfaces.
Frontend Libraries and Frameworks
To speed up development, developers often rely on frontend frameworks and libraries. They help developers code faster, save time, and create better user experiences.
Some of the most popular options include:
- AngularJS: A powerful tool for building fast, dynamic single-page applications (SPAs) with JavaScript. It makes HTML dynamic, supports data binding, and scales applications easily.
- React.js (ReactJS): A flexible, component-based JavaScript library created by Facebook. It focuses on building user interfaces, making websites more responsive and engaging.
- Bootstrap: A free, open-source framework for creating mobile-first websites. Using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, it speeds up frontend development and provides modern page structures.
- jQuery:Query simplifies JavaScript coding, helping developers handle tasks quickly and efficiently. It makes DOM manipulation easier, handles browser events, supports animations, enables Ajax, and ensures cross-browser compatibility.
- Sass: A CSS preprocessor that streamlines styling. With features like variables, nesting, and inheritance, it lets developers create clean, efficient, and scalable code
Other popular tools such as Semantic-UI, Foundation, Materialize, Backbone.js, and Ember.js are also used to improve website structure, enhance user interfaces, and create interactive designs.
2. Backend Technologies in Full Stack Development
Backend technologies are critical for full-stack development and Web Development. They focus on server-side development, making sure website functionality runs smoothly.
The back end handles database management, processes queries, and responds to client-side commands. Each pillar has its specific responsibilities and plays a key role in delivering a smooth user experience.
The back end is built using several languages, libraries, and frameworks. Let’s explore them.
Backend Languages and Tools

- PHP: PHP stands out as a leading choice for server-side programming. It runs code on the server, making it ideal for backend programming and building web applications.
- C++: C++ is a general-purpose programming language. While it is often used in competitive programming, it also works as a backend language for web applications.
- Java: Java is designed to handle large-scale, high-performance backend applications. With its prebuilt components, it’s a strong choice for developing big web projects.
- Python: Python is a flexible language that lets developers create and link backend services with speed and ease.
- Node.js: Node.js is credited with taking JavaScript out of the browser and into the server. Keep in mind, Node.js isn’t a framework or a language on its own. Instead, it is a runtime environment widely used for backend services such as APIs for web and mobile applications. Companies like PayPal, Uber, Netflix, and Walmart rely on it for their backend systems.
Backend Frameworks
Frameworks make server management and backend programming easier. Popular options include Express, Django, Rails, Laravel, and Spring. These frameworks improve web application functionality and speed up the overall development process.
Other Backend Languages
Beyond the core languages, developers also use C#, Ruby, Go, and REST for backend development. These technologies support database management, server-side programming, and backend coding for modern web projects.
Full Stack Development Stacks
Full-stack tools bring simplicity and speed to web application development. They allow developers to create robust, flexible, and dynamic apps using JavaScript on both the front end and back end. The MERN and MEAN stacks stand out as the most popular choices.
1. MERN Stack
Popular in full-stack development, the MERN stack helps developers create web apps quickly and effectively.Since it uses JavaScript on both the frontend and backend, developers can create scalable and powerful applications with ease.
Key components include:
- MongoDB: A non-relational database for storing application data.
- Express: A Node.js web server for building backend services.
- React:React helps developers build interactive and easy-to-use web interfaces with JavaScript.
- Node: A JavaScript runtime for building server-side applications.
2. MEAN Stack
The MEAN stack is a JavaScript-based framework that makes building full-stack apps simple and fast. It simplifies development and speeds up deployment while keeping integration smooth, since all its technologies use JavaScript.
Key components include:
- MongoDB: An open-source, non-relational, document-oriented database.
- Express.js: A framework to build organized Node.js APIs with routes and middleware.
- Angular.js: An open-source framework for developing responsive single-page web apps.
- Node.js: A runtime environment that supports high-performance, scalable backend apps across platforms.
What is Web Development?
Web Development is about designing and building websites.Web developers usually work with: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
They ensure websites:
- Look great
- Load fast
- Deliver smooth user experiences
In short, web developers ensure websites look great, load fast, and give a smooth user experience.
Who Are Web Developers?
Web developers are experts in making websites that work smoothly and keep users engaged. Their role goes beyond just writing code—they make sure every website delivers a smooth and seamless browsing experience for users.
They design and test websites using core languages like JavaScript, HTML, and XML. Web developers also work closely with teams, collaborating with designers, developers, and stakeholders to achieve the best results.
In addition, they incorporate multimedia content, test application functionality, and troubleshoot any issues that might affect performance or user experience.
Skilled web developers manage both frontend and backend coding with modern web technologies. They also handle regular website maintenance and refine designs to keep interfaces functional, attractive, and user-friendly.
Technologies in Web Development
Web development uses a variety of tools and programming languages to build websites. One of the most crucial areas is frontend development.
Frontend development focuses on the client side. It deals with visual elements and interactive elements that users see and engage with. A strong front end ensures a smooth user experience and attractive interfaces.
1. Frontend technologies in web development
The key concept behind frontend development is HTML and CSS— these languages are used for structuring and styling the web pages.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) HTML provides the basic structure for websites, shaping how content is arranged and displayed.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) styles the content. It controls colors, fonts, layouts, and overall design.
The magic behind interactive websites is JavaScript. It enables:
- Interactive elements
- User input handling
- DOM manipulation
- Asynchronous communication with servers
Beginners usually start with variables, functions, data types, control flow, and event handling. Later, they learn DOM manipulation, AJAX, and frameworks to build complex web applications.
Frontend Frameworks and Libraries
Front-end frameworks and libraries give developers ready-made code and tools to work faster. They help speed up development, improve efficiency, and prevent repetitive coding.
Some of the most popular options include:
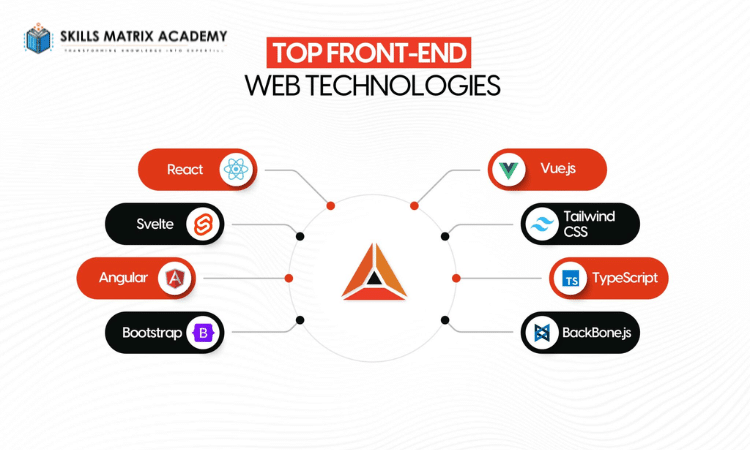
- React: A JavaScript library used to build websites and single-page applications (SPAs). It relies on reusable components, which improve both performance and user experience.
- Angular: A framework supported by Google that uses TypeScript to build powerful web applications. It offers features like dependency injection, routing, and state management, which make it perfect for building dynamic apps
- Vue.js :Vue.js is a lightweight JavaScript framework for creating smooth and responsive single-page apps.It combines reactive data with modular components, giving developers a smooth and efficient frontend coding experience.
- jQuery: Simplifies tasks such as working with HTML, handling events, creating animations, and using AJAX in web projects.
- Bootstrap: Provides pre-styled layouts and components that speed up responsive design. It makes it easier to create mobile-first and modern websites quickly.
- Backbone.js is a minimal JavaScript framework designed to help developers create organized web applications. It offers models with key-value data binding, collections with a powerful API, and views that handle events efficiently.
Backend Development is all about server-side programming. It handles the logic, database interactions, and server management of web applications. Backend developers write code on the server to process client-side requests, manage databases, and generate dynamic content.
They use languages like Python, Ruby, PHP, and frameworks such as Node.js, Django, and Flask to build robust and scalable server-side applications.
Backend Programming Languages
Backend developers use versatile programming languages to build reliable and scalable applications.
Some of the most common ones include:
- Python:Python is an easy-to-learn, flexible language that makes coding simple and efficient.It adapts to multiple coding styles—procedural, object-oriented, and functional—making it a favorite among developers.
- From web development and data analysis to AI, scientific research, and automation, Python powers it all. With its rich standard library and countless packages, it’s a go-to choice for building a wide range of applications.
- Ruby:Ruby is a dynamic, object-oriented language designed to keep coding simple and enjoyable for developers.. With Ruby on Rails, the most popular web framework, developers can build applications faster by using ready-made solutions for everyday tasks.
- PHP: PHP is a server-side scripting language commonly used in web development. It can be embedded into HTML, executed on the server, and used to generate dynamic web pages. PHP also interacts with databases and handles user input, making it a reliable choice for backend systems.
Backend Frameworks & Libraries
Frameworks and libraries are essential for backend development as they speed up the process and promote cleaner, reusable code.
Django Django is a most popular Python framework that allows the developers to quickly build web applications with clean and reusable code.
Express is a lightweight framework that helps developers create web apps and APIs efficiently, offering built-in features to simplify the process.
Laravel is a PHP framework that provides built-in tools for routing, authentication, and caching. Its clean code and ease of use make it popular among developers.
Other options, such as Flask (Python) and Spring Boot (Java), offer additional features for routing, authentication, and database management, giving developers more flexibility.
Version Control
Version control is a must in web development. It manages code changes, tracks project history, and enables teamwork.
Tools like Git allow:
- Branching for feature development
- Merging to combine changes
- Distributed collaboration across teams
- Efficient code management to revert, compare, and resolve conflicts
Database Management
Database management handles the storage, retrieval, and security of data in web apps.
Developers use SQL or NoSQL databases with management systems to:
- Create, query, update, and delete data
- Maintain data integrity
- Ensure data security and reliability.
- The back end connects with databases to handle requests and deliver dynamic content.
Responsive Design
Responsive design allows websites to fit and look good on any device or screen size.
Key techniques include:
- Flexible layouts
- Fluid grids
- Media queries
This improves user experience, readability, and navigation across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices.
APIs and Integration
APIs connect applications to external services.
Developers use RESTful APIs or GraphQL to:
- Fetch and display data
- Build interactive apps
- Enable communication across multiple platforms.
- APIs let modern apps access data and features from different services in real time.
Testing and Debugging
Testing and debugging keep applications reliable and functional.
Developers use tools and methods to:
- Identify errors
- Fix issues quickly
- Ensure performance across environments and interactions.
- Regular testing ensures apps remain secure and high-performing.
Deployment and Hosting
Deployment and hosting bring your app online, making it live and ready for users.
Platforms like Heroku, Netlify, and AWS help developers:
- Manage servers
- Keep apps secure and fully functional.
- Ensure responsive performance with no interruptions.
- With proper deployment, apps stay scalable, efficient, and user-ready.
Which route is betterFull Stack Development OR Web Development: ?
Choosing between Full Stack Development and Web Development depends on your interests and career goals.
At first, it may seem like these roles are clearly separated. Web developers often focus on frontend tasks like design and user interfaces.
Full-stack developers, on the other hand, handle both frontend and backend—covering the entire website architecture.
Today, the line is blurring. Companies running projects that cover different parts of a website often choose full-stack developers.










